Szczepienia przed ciążą

Niektóre zakażenia przebyte w czasie ciąży mogą prowadzić do wad wrodzonych u dziecka, takich jak opóźnienie rozwoju, choroby serca, upośledzenie słuchu, problemy ze wzrokiem, deformacje, a nawet śmierć. Zadbanie o to, aby wszystkie szczepienia były aktualne i poddanie się szczepieniom, które mogą okazać się konieczne przed zajściem w ciążę, może zapobiec niektórym z najpoważniejszych zagrożeń dla dziecka.
Różyczka
Różyczka to zakażenie wirusowe. Jest to choroba o łagodnym przebiegu, która u zdrowych osób powoduje wysypkę i powiększenie węzłów chłonnych. W przypadku zachorowania na różyczkę w ciągu pierwszych trzech miesięcy ciąży, istnieje większe prawdopodobieństwo, że choroba będzie miała ciężki przebieg. Z dużym prawdopodobieństwem ciąża zakończy się poronieniem lub urodzeniem dziecka z wrodzonymi anomaliami znanymi jako zespół różyczki wrodzonej (CRS).
Zakażenie różyczką w pierwszych trzech miesiącach ciąży skutkuje poronieniem w 20% przypadków.
Zespół różyczki wrodzonej powoduje powikłania u 85% dzieci, których matki zachorowały na różyczkę w pierwszych trzech miesiącach ciąży. Do takich powikłań należą głuchota, zaćma, wady serca, zaburzenia mózgu, opóźnienie rozwoju oraz uszkodzenie narządów. U dzieci urodzonych z CRS może rozwinąć się cukrzyca i zaburzenia czynności tarczycy w późniejszym okresie życia.
Przed zajściem w ciążę warto sprawdzić ważność szczepienia, ponieważ w trakcie ciąży przyjęcie szczepionki przeciwko różyczce jest niemożliwe. Należy porozmawiać z lekarzem i sprawdzić krajowe wytyczne dotyczące szczepień.
Najważniejsze fakty dotyczące różyczki, objawów, powikłań, czynników ryzyka, sposobu rozprzestrzeniania się, profilaktyki i leczenia.
Ospa wietrzna
Chociaż 90% przypadków ospy wietrznej występuje u dzieci, skutki działania wirusa są poważniejsze u dorosłych. Zachorowanie na ospę wietrzną w czasie ciąży może powodować poważne schorzenia i podwyższone ryzyko poronienia, zespołu wrodzonej ospy wietrznej lub ospy noworodkowej, gdy dziecko urodzi się w aktywnej fazie zakażenia.
Zespół wrodzonej ospy wietrznej powoduje poważne, trwałe upośledzenie fizyczne i intelektualne, a także problemy skórne.
Szczepienie może zapobiec wystąpieniu ospy wietrznej i jej powikłań. Osoby, które nie przebyły ospy wietrznej lub nie były zaszczepione przeciwko niej przed zajściem w ciążę, powinny porozmawiać z lekarzem i sprawdzić krajowe wytyczne dotyczące szczepień.
Najważniejsze fakty dotyczące objawów, powikłań, czynników ryzyka, sposobu rozprzestrzeniania się, profilaktyki i leczenia ospy wietrznej (varicella).
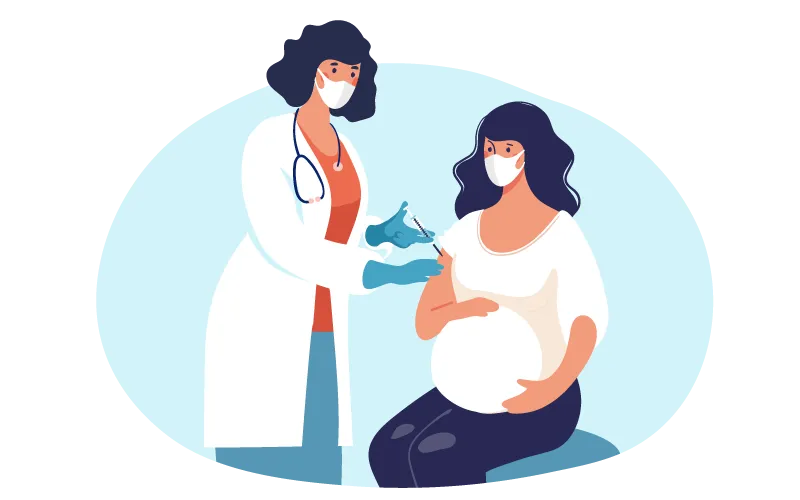
Szczepienie kobiety ciężarnej chroni ją przed potencjalnie ciężkimi chorobami i powikłaniami w okresie ciąży, a także może pomóc ochronić nowo narodzone dziecko.

Dowiedz się, w jaki sposób szczepionki mogą chronić rodziców i ich dzieci i jakie szczepionki mogą być stosowane przed ciążą, w jej trakcie i po ciąży.
